This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
CLINICAL CASE
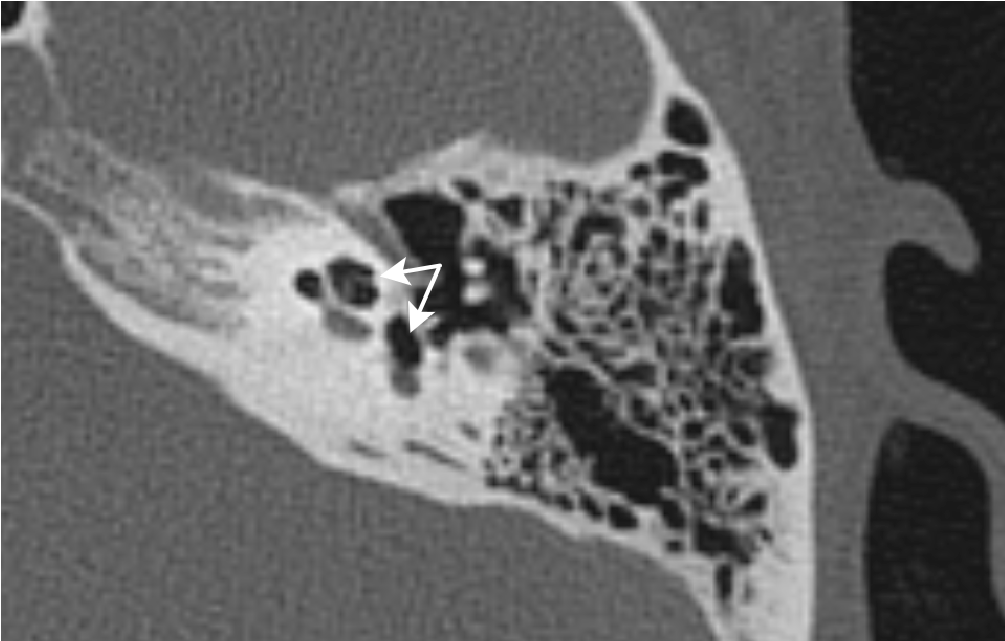
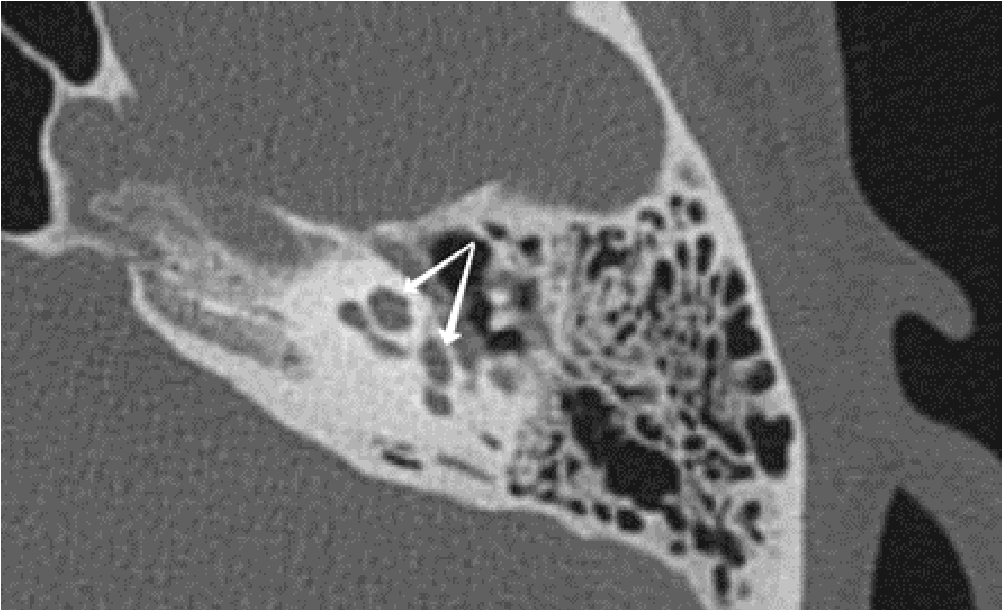
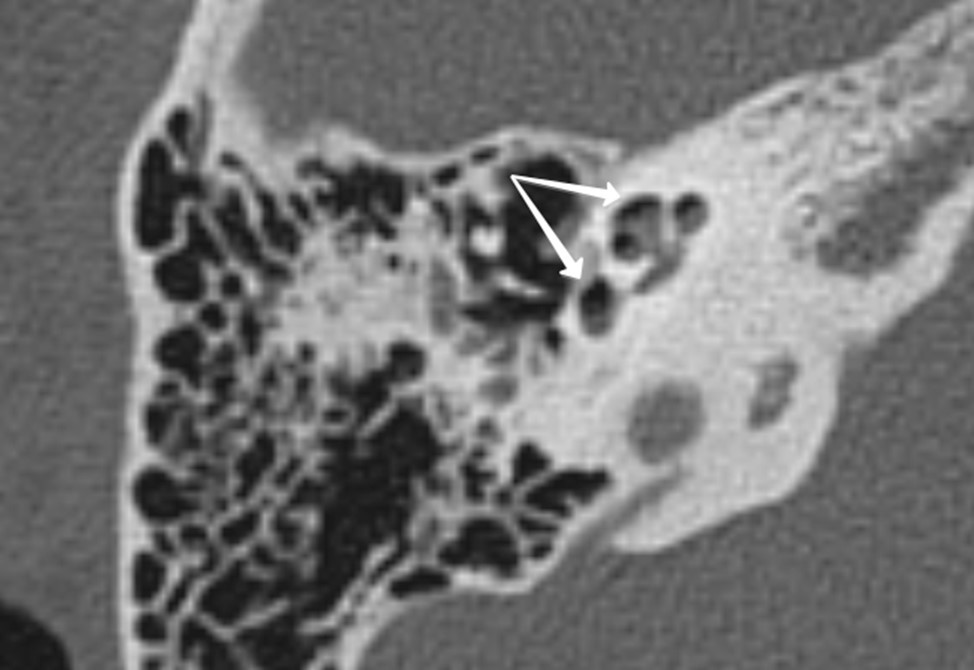
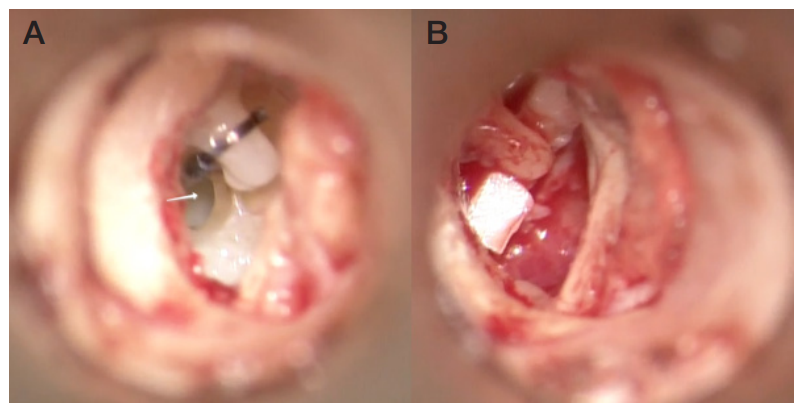
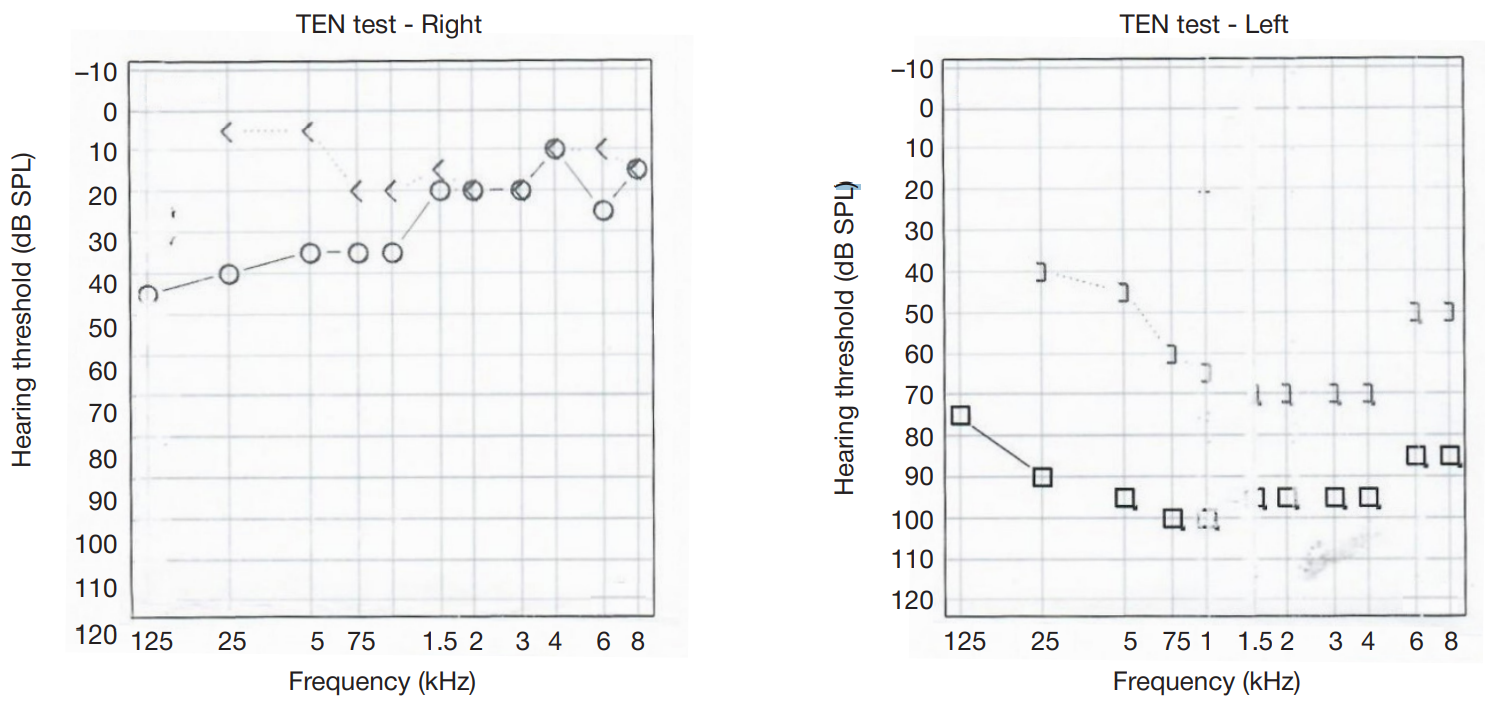
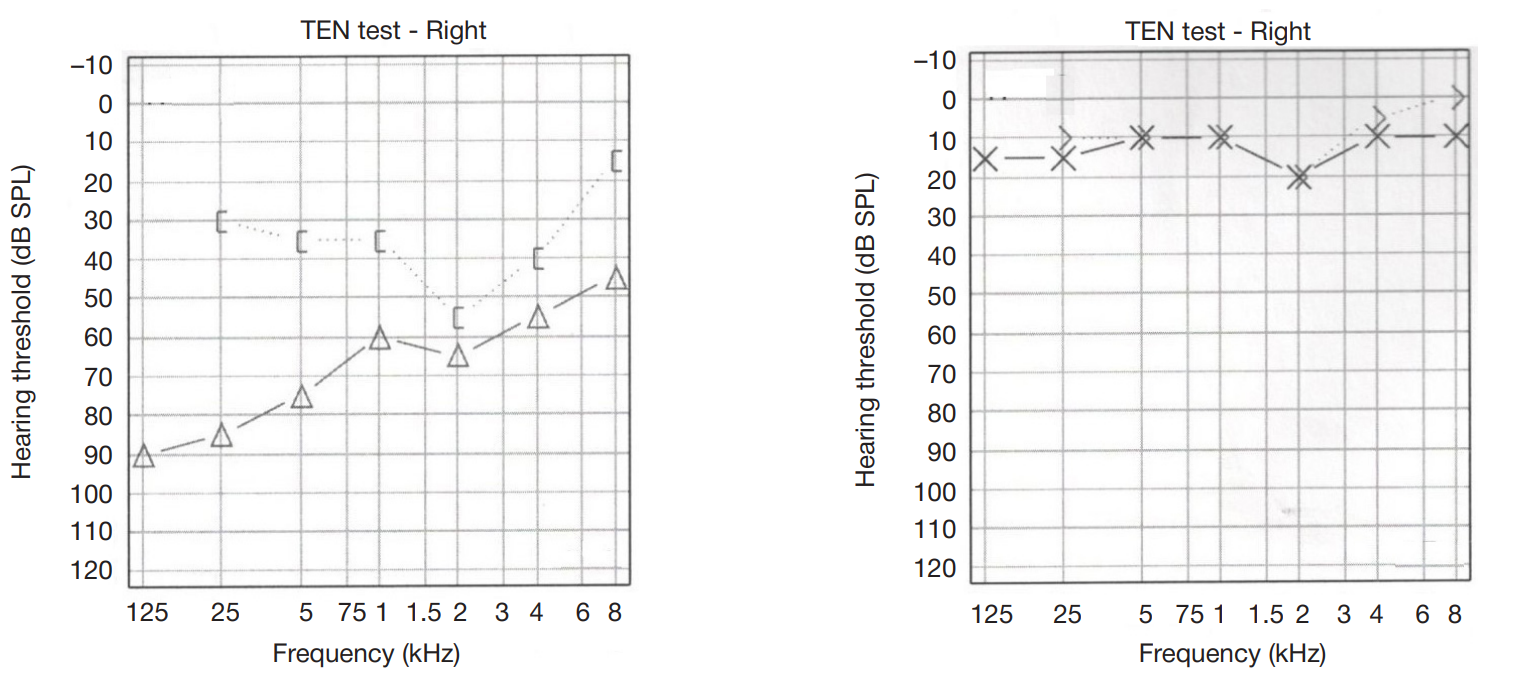
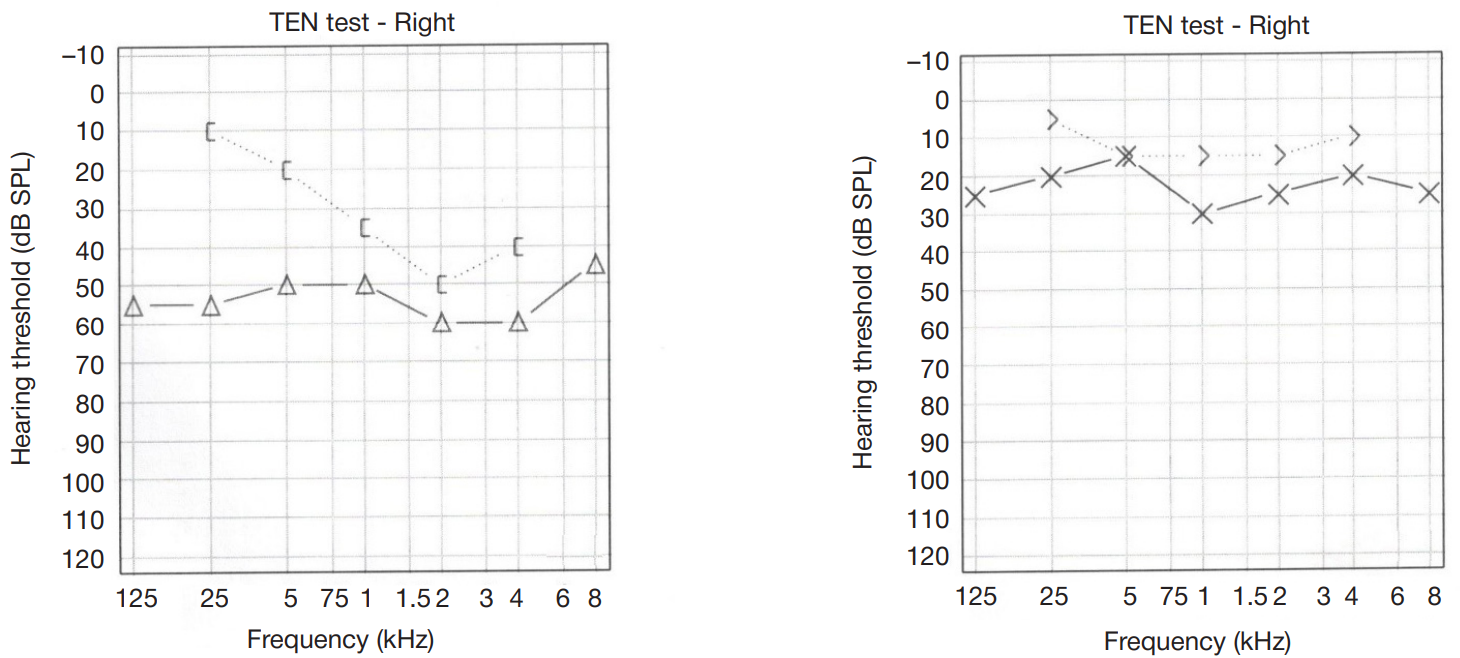
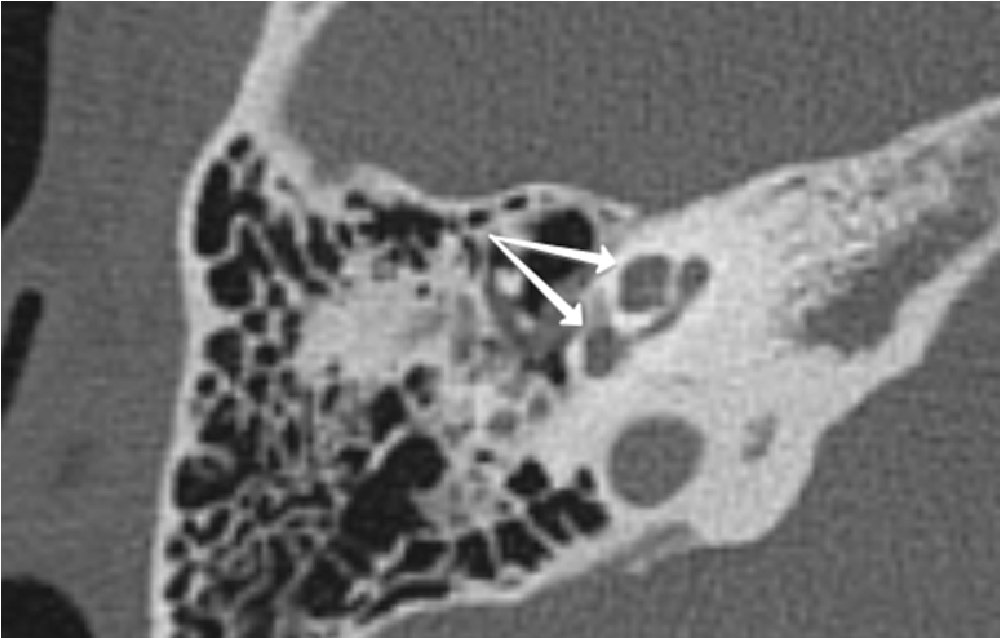
Pneumolabyrinth as a postoperative complication of stapedoplasty
1 National Medical Research Center for Otorlaryngology of Federal Medical Biological Agency, Moscow, Russia
2 Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Khassan M. A. Diab
Volokolamskoe shosse, 30, str. 2, Moscow, 123182, Russia; ur.liam@baidnasah
Author contribution: Diab KhMA — research design, surgical treatment of patients, manuscript editing; Daikhes NA — manuscript editing; Pashchinina OA, Zukhba AG — manuscript writing; Kokhanyuk SV, Pirogova NE — literature review.
Compliance with ethical standards: the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the National Medical Research Center for Otorhinolaryngology of FMBA (protocol № 03/22 dated June 20, 2022). The patients submitted the informed consent to surgery and personal data processing.