This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
CLINICAL CASE
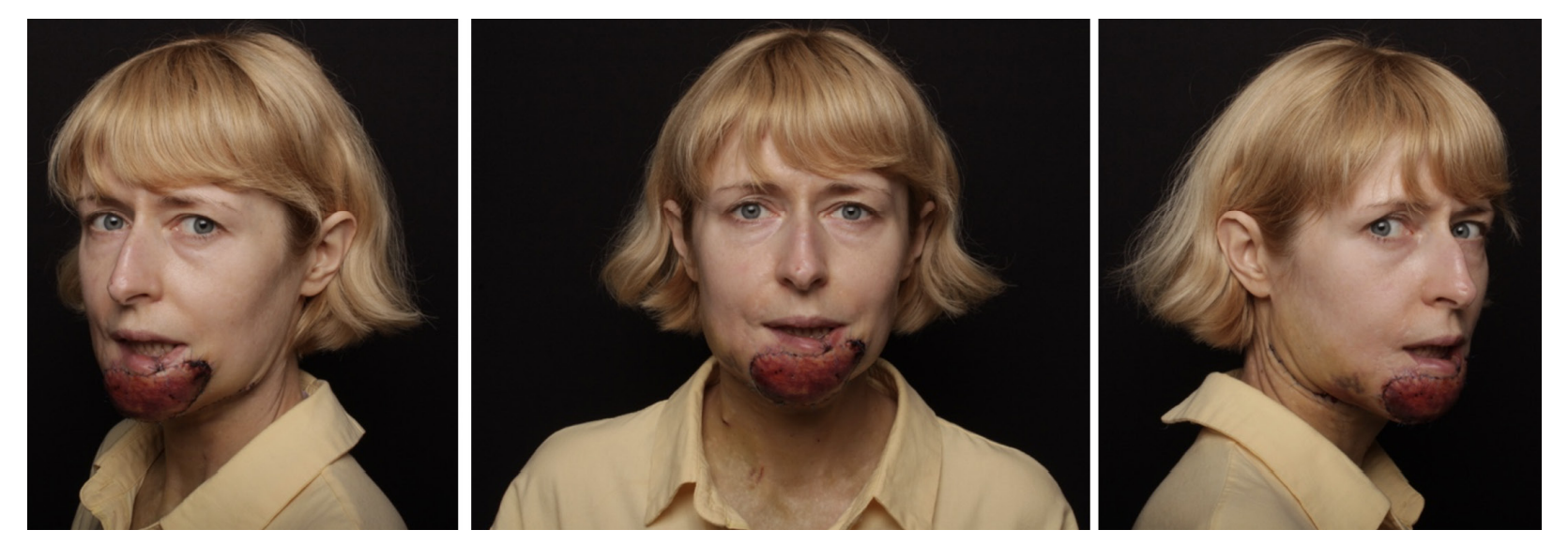
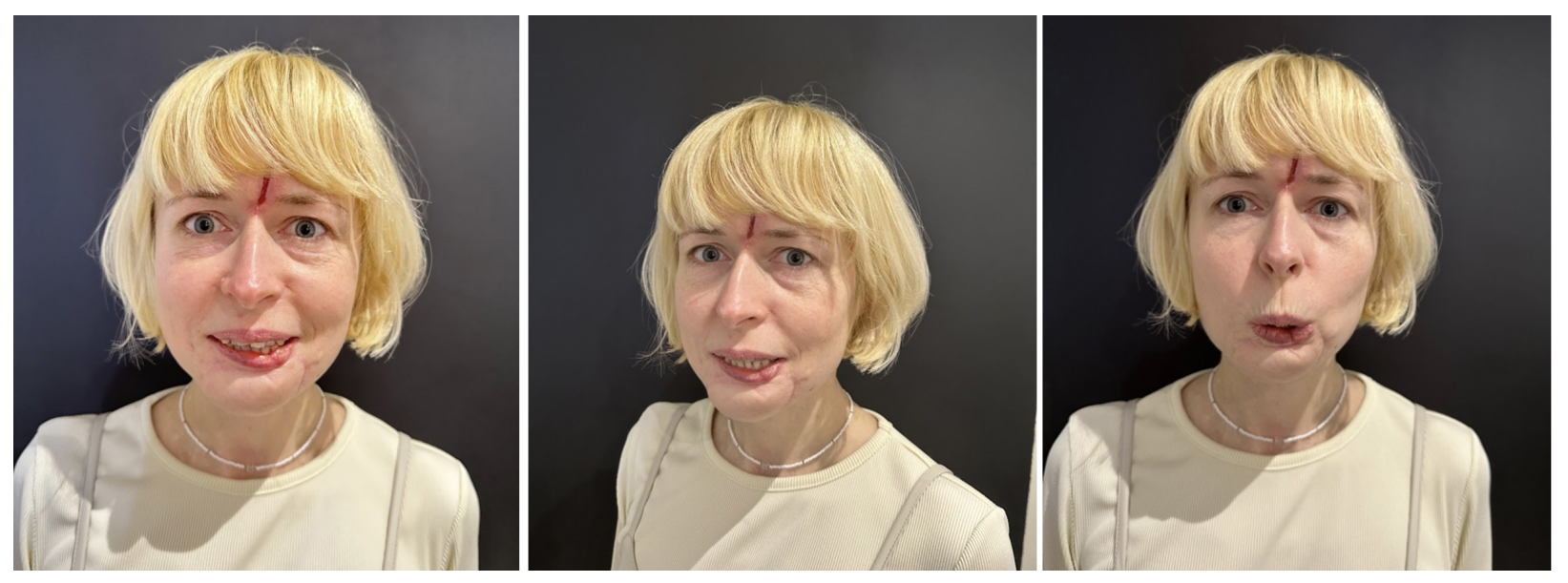
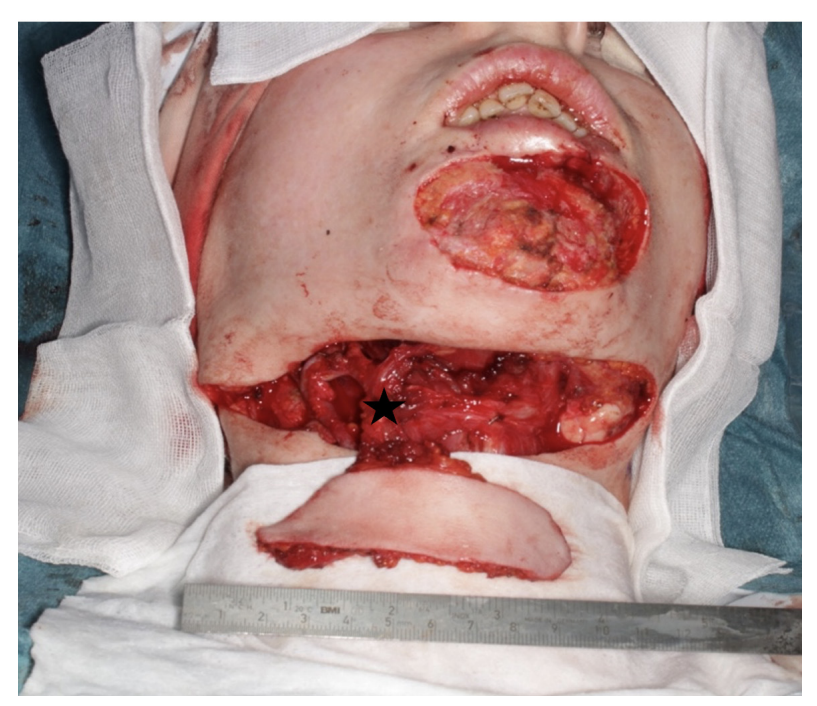
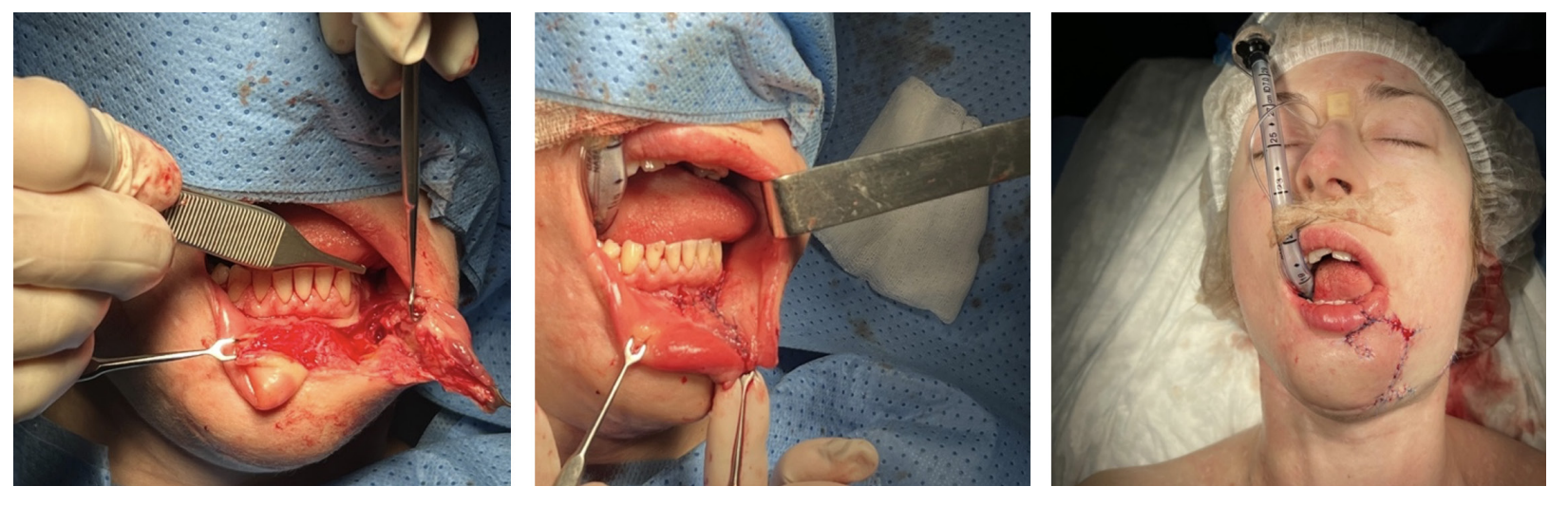
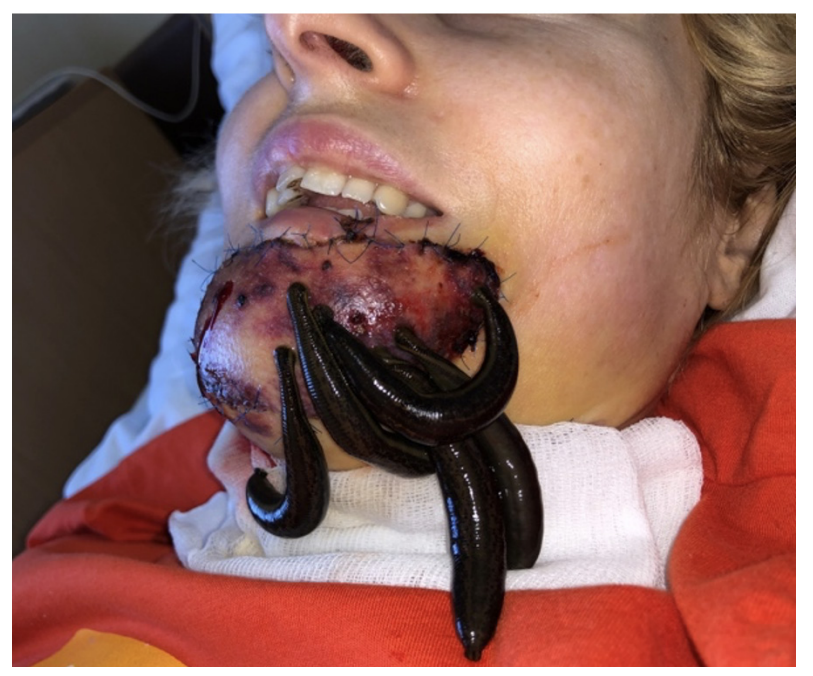
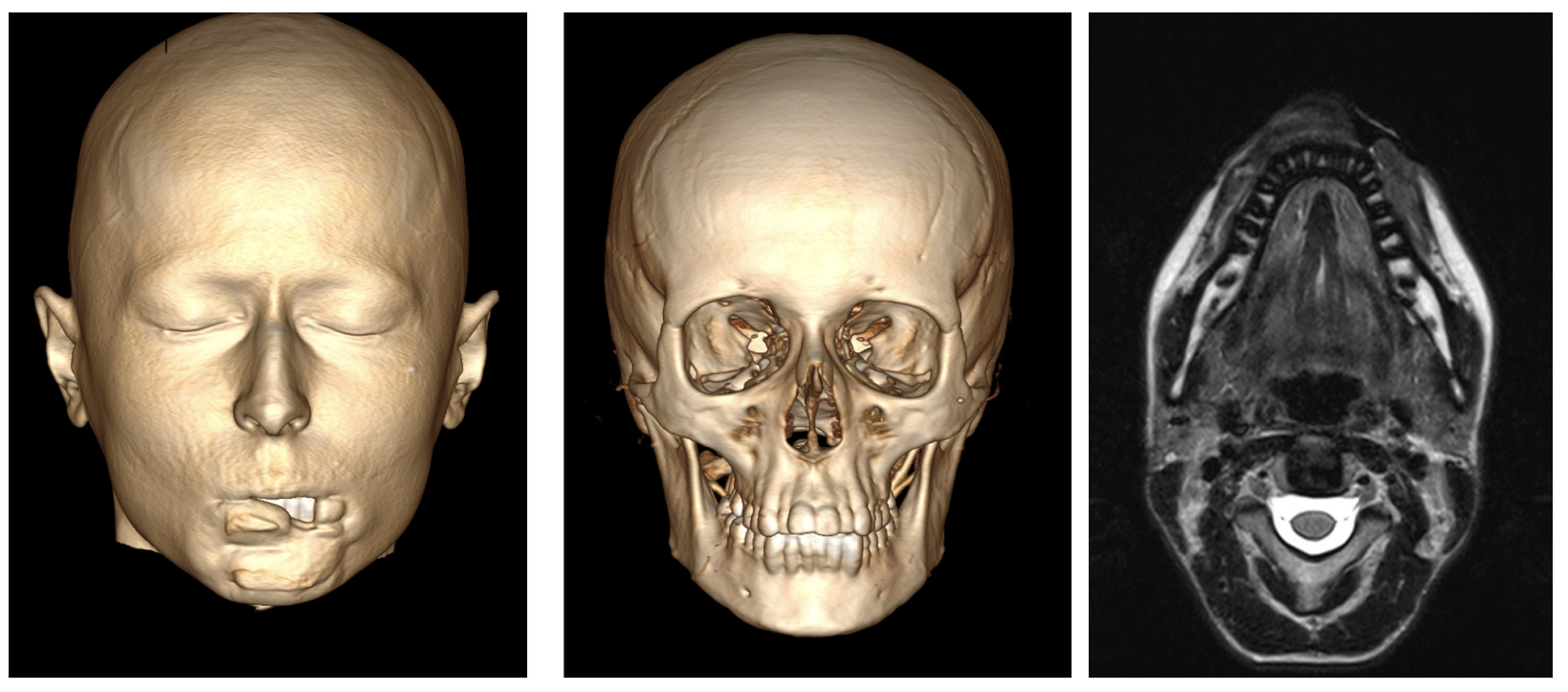
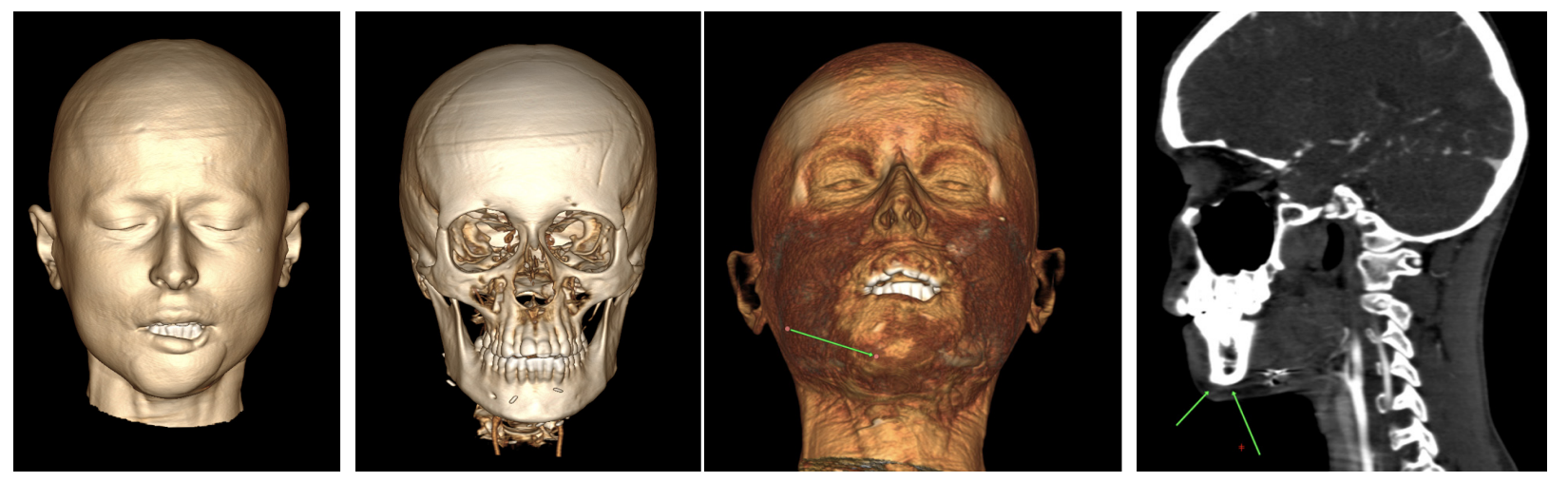
Possibility of using submental flap for lower lip reconstruction
1 Federal Clinical Center for High Medical Technologies of the Federal Medical Biological Agency, Moscow, Russia
2 National Medical Research Center for Otorlaryngology of Federal Medical Biological Agency, Moscow, Russia
3 Academy of Postgraduate Education, Federal Scientific and Clinical Centre for Specialized Types of Medical Care and Medical Technologies of the Federal Medical Biological Agency, Moscow, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Arbak А. Khachatryan
Volokolamskoe shosse, 30, bld. 2, Moscow, 123182, Russia; ur.xednay@kabrard
Author contribution: Danishchuk OI, Nazarian DN — surgical procedure, manuscript writing and editing; Karpova EI — surgical procedure; Khachatryan AA — manuscript writing; Razmadze SS — patient management, manuscript writing.
Compliance with ethical standards: the informed consent to case study publication was submitted by the patient.