This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
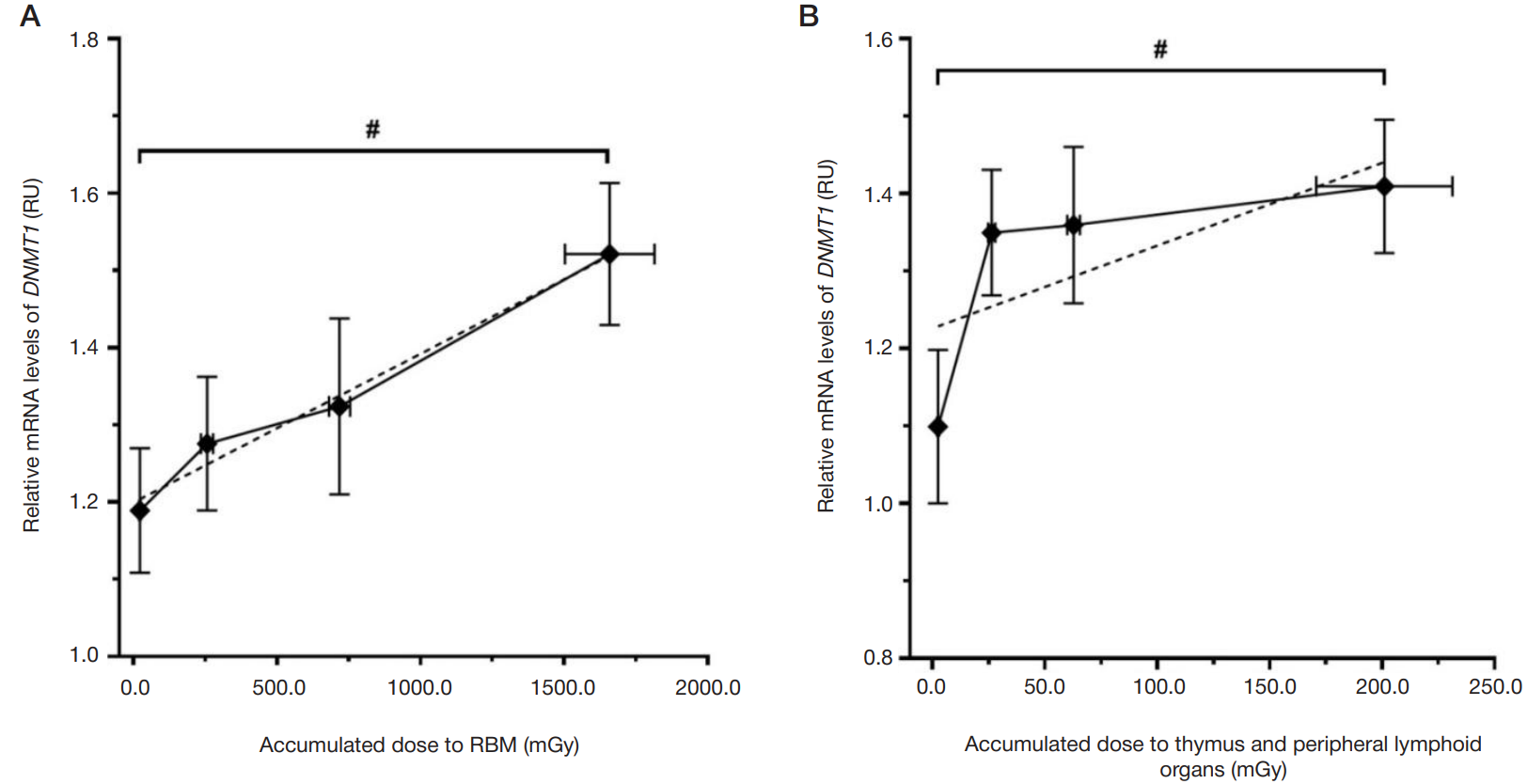
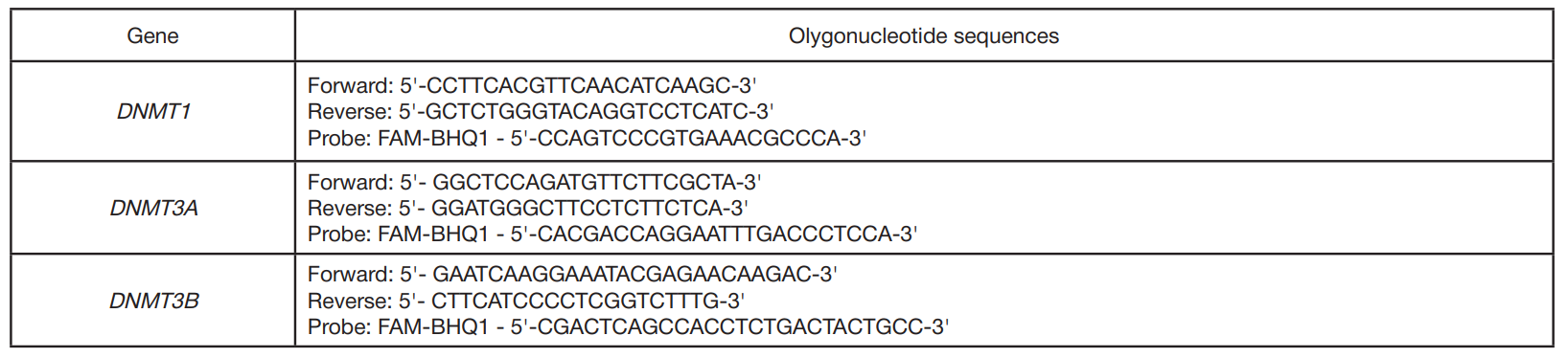
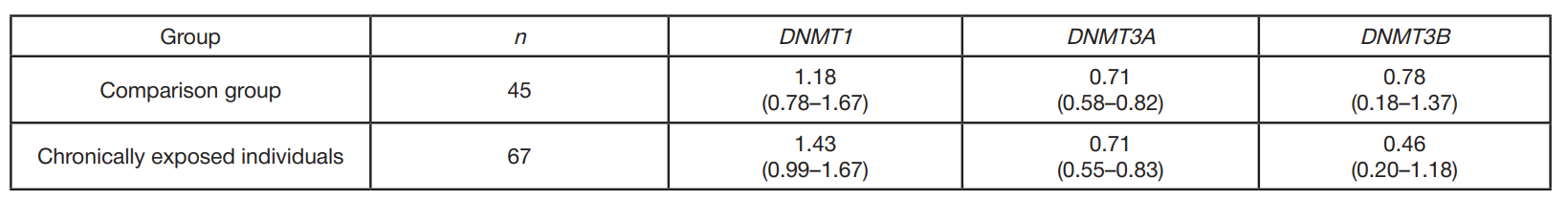
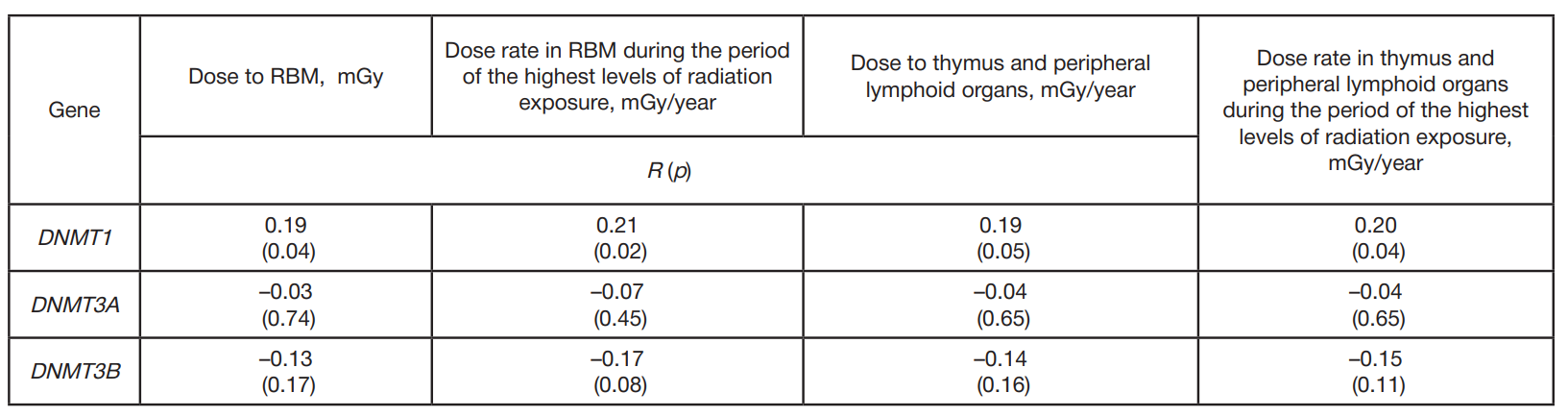
Transcriptional activity of DNA-methyltransferase genes in the chronically exposed residents of the Ural region
1 Urals Research Center for Radiation Medicine of the Federal Medical Biological Agency, Chelyabinsk, Russia
2 Chelyabinsk State University, Chelyabinsk, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Vladislav S. Nikiforov
Vorovskogo, 68, korp. 1, Chelyabinsk, 454141, Russia; ur.liam@xvorofikin
Funding: the study was supported by the Federal Medical Biological Agency of Russia (Government contract № 27.501.21.2 of June, 11 2021).
Author contribution: Nikiforov VS — laboratory tests, statistical analysis, manuscript writing; Blinova EA, Akleyev AV— study planning, manuscript editing and preparing the final version of the article.
Compliance with ethical standards: the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Urals Research Center for Radiation Medicine of FMBA of Russia (protocol № 3 dated June 28, 2022). The informed consent was submitted by all patients.