This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
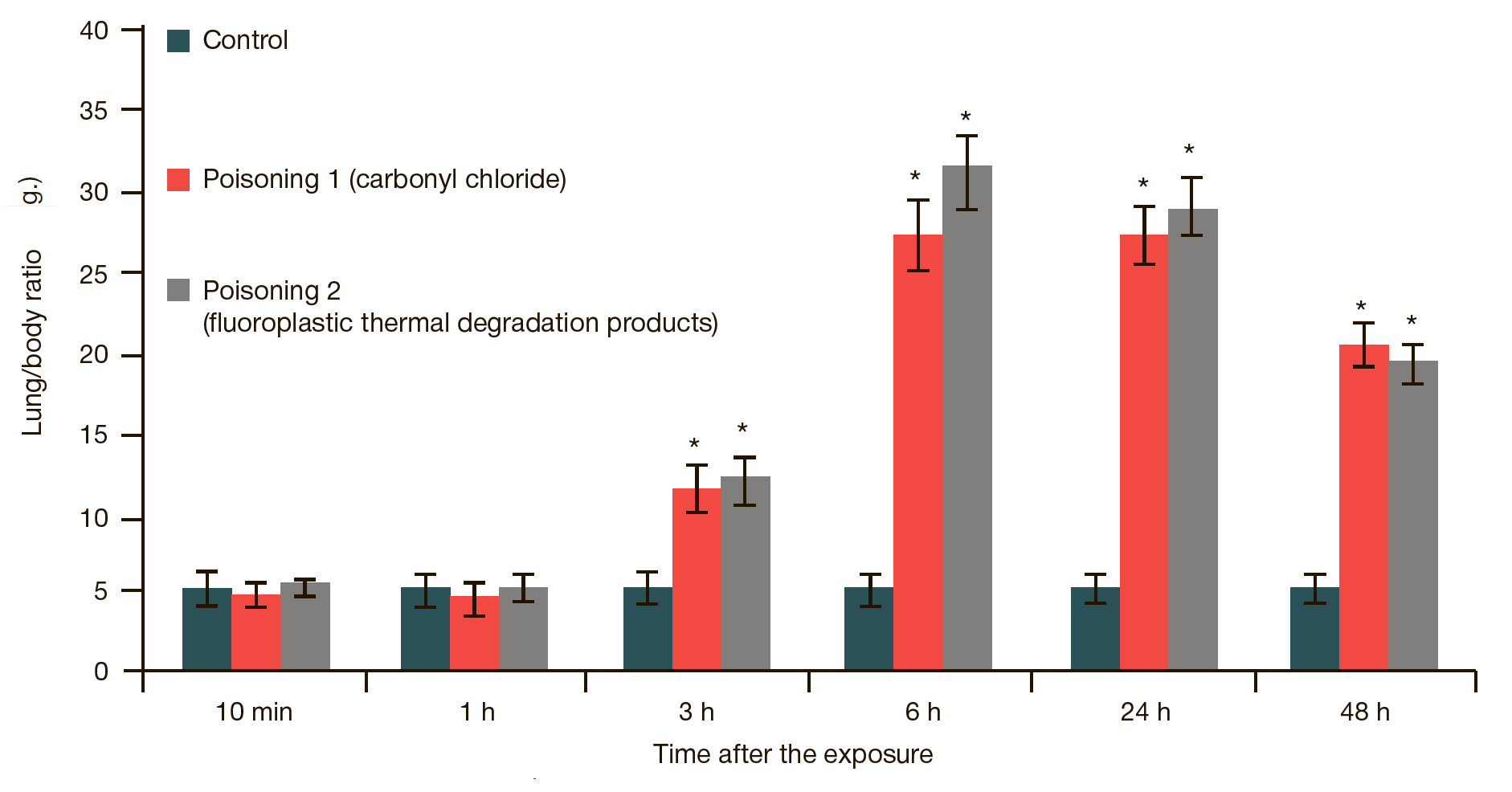
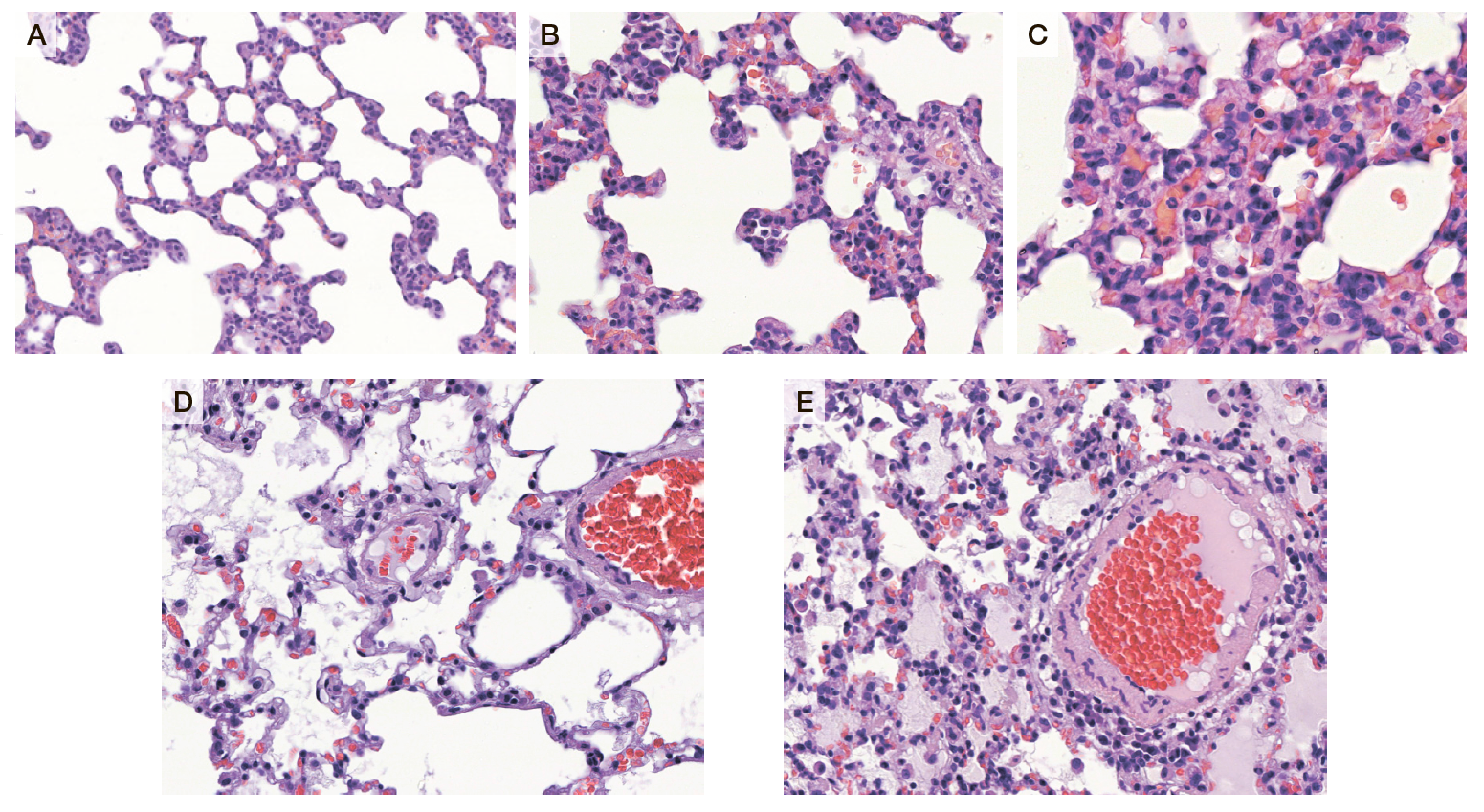
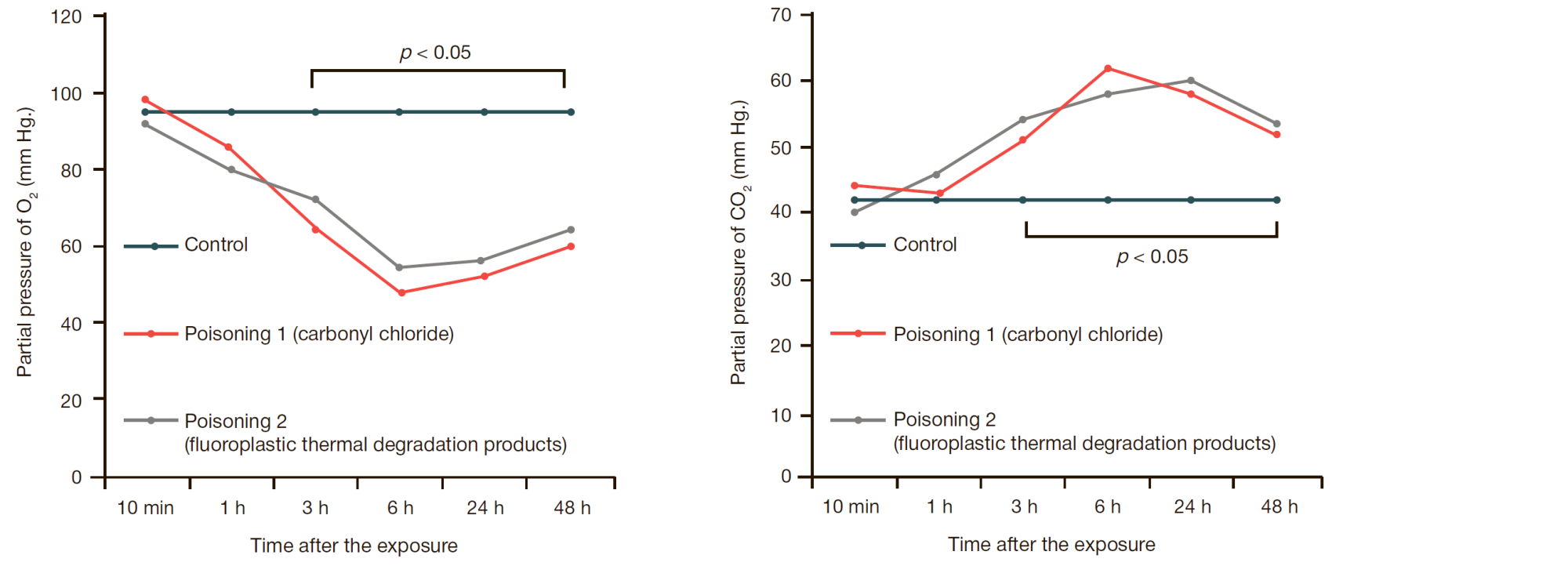
Comparative assessment of toxic pulmonary edema caused by poisoning with carbonyl chloride and fluoroplastic thermal degradation products
1 Kirov Military Medical Academy of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
2 State Scientific Research Test Institute of the Military Medicine of Defense Ministry of the Russian Federation, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Dmitry M. Yaroshenko
Akademika Lebedeva, 6, Saint-Petersburg, 194044, Russia; ur.xednay@bps-oknehsoray
Author contribution: Yaroshenko DM — experimental part of the study, processing of experimental study results, manuscript writing; Lopatko VS — literature review, technical data processing, manuscript writing; Tolkach PG — interpretation of the results, manuscript writing; Vengerovich NG — interpretation of the results, manuscript editing; Basharin VA — research concept, determining the main directions of the study, manuscript editing.
Compliance with the ethical standards: the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kirov Military Medical Academy of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (protocol No. 288 dated 20 February 2024). The research procedure was guided by the requirements of the regulatory legal acts on conducting animal experiments, including humane handling of animals (Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes).