This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
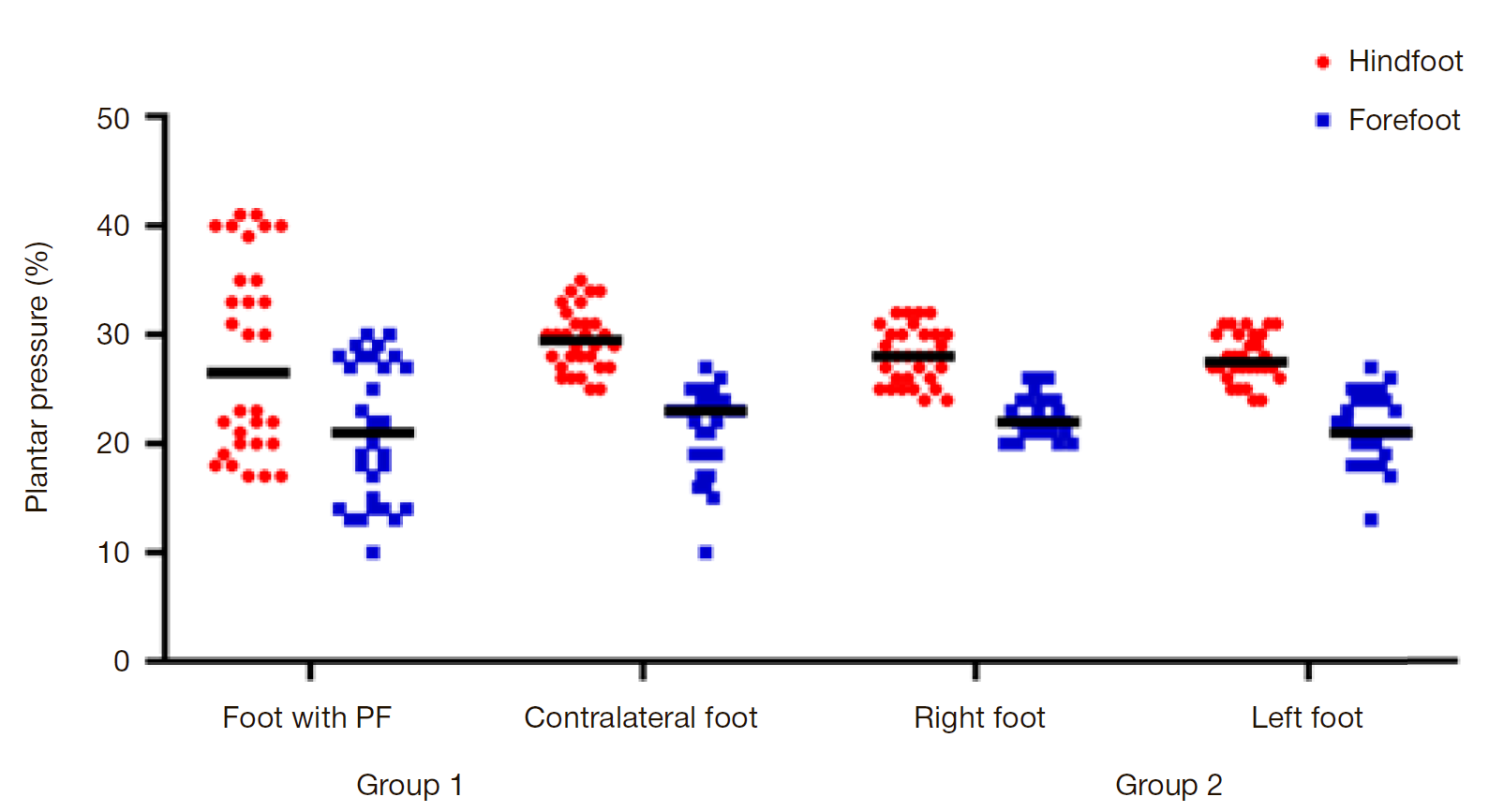
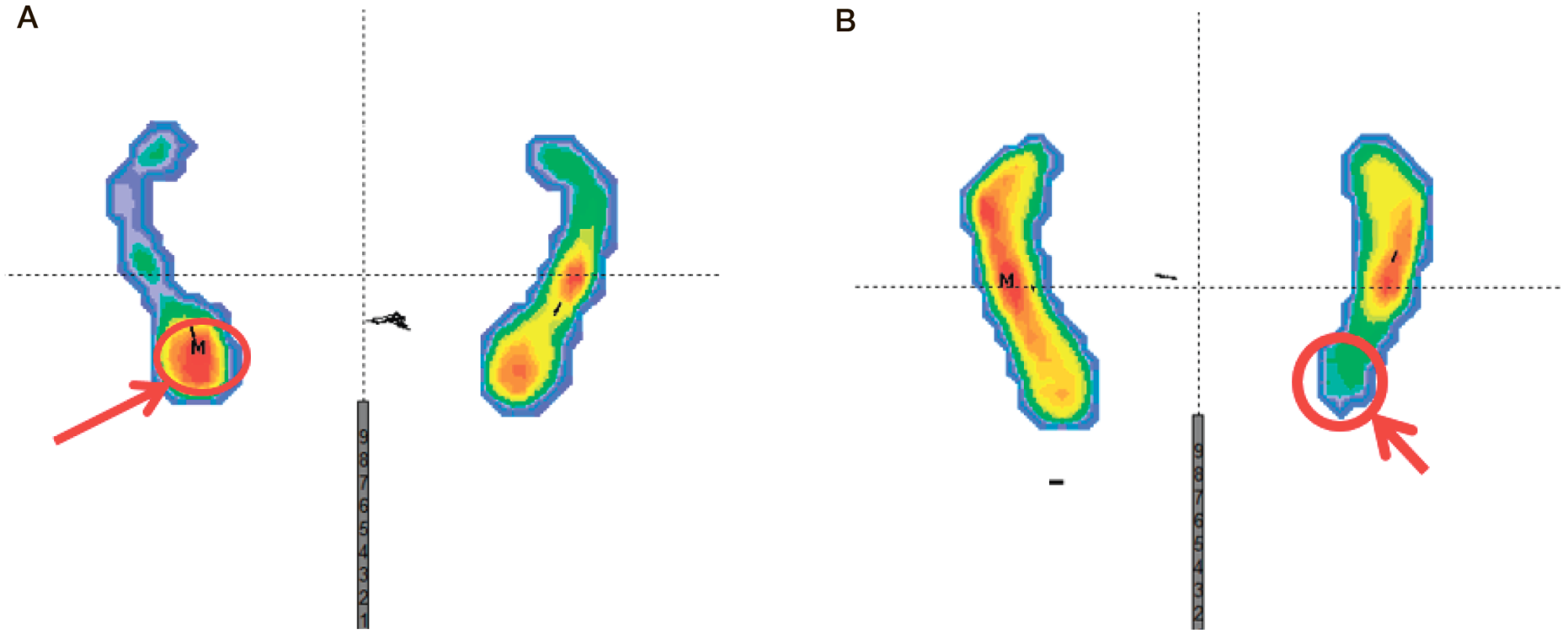
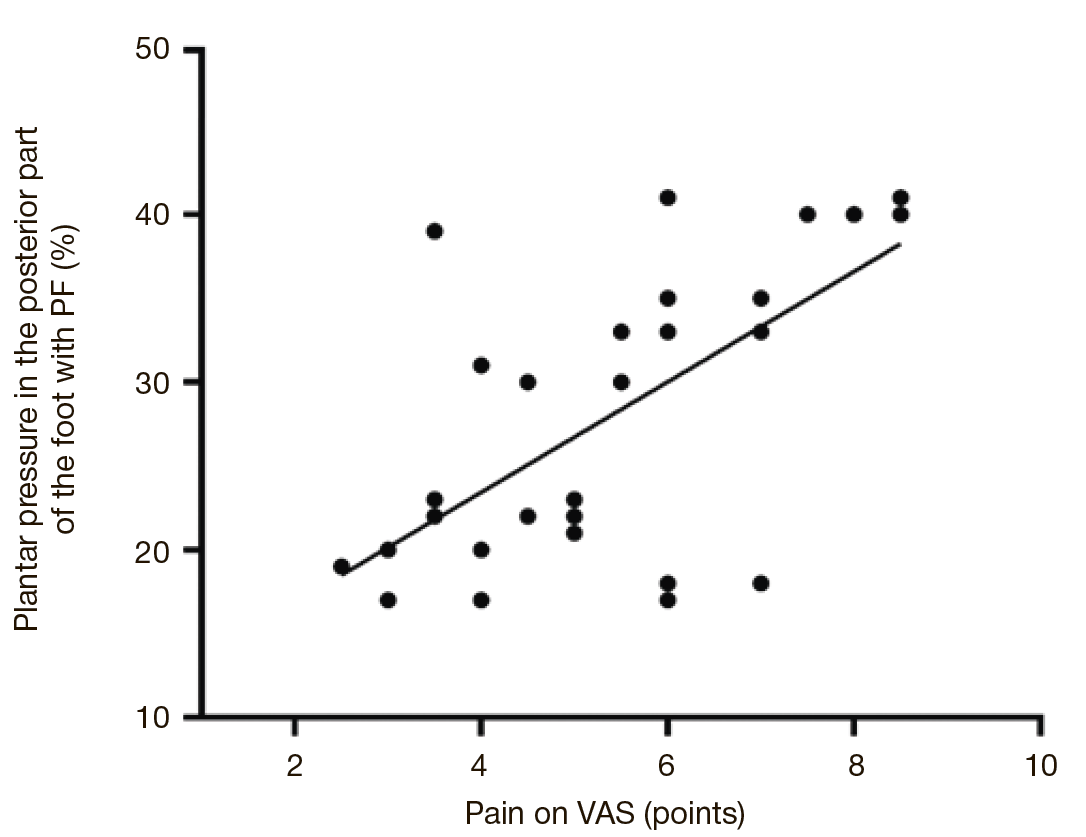
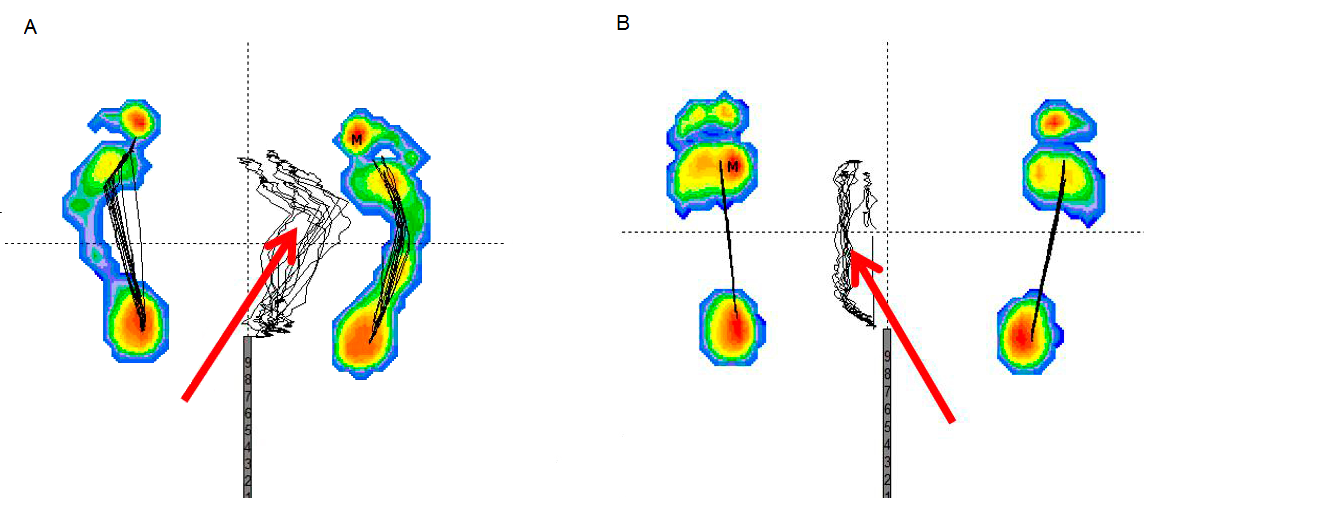
Plantar pressure distribution features in athletes with plantar fasciitis
1 Federal Research and Clinical Center for Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation of the Federal Medical Biological Agency, Moscow, Russia
2 Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Anton V. Slivin
B. Dorogomilovskaya, 5, Moscow, 121059, Russia; ur.liam@nivils-notna
Author contribution: Karmazin VV — study concept and planning, research data acquisition and analysis, manuscript editing; Slivin AV — research data acquisition and analysis, statistical data processing, manuscript writing, formatting; Parastaev SA — editing, approval of the final version of the article.
Compliance with the ethical standards: the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University (protocol No. 225 dated 23 January 2023). All athletes submitted the consent to study participation.