This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
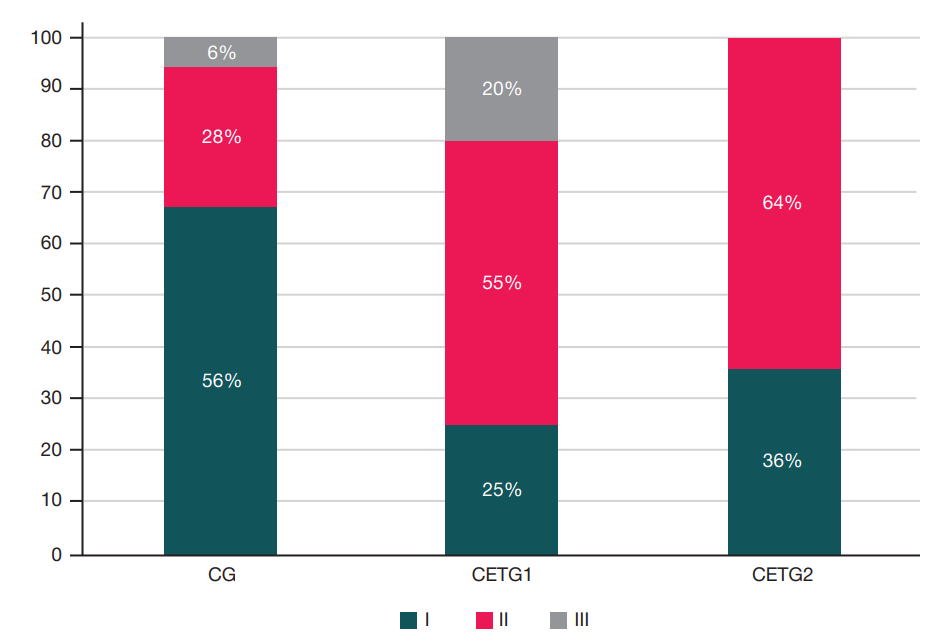
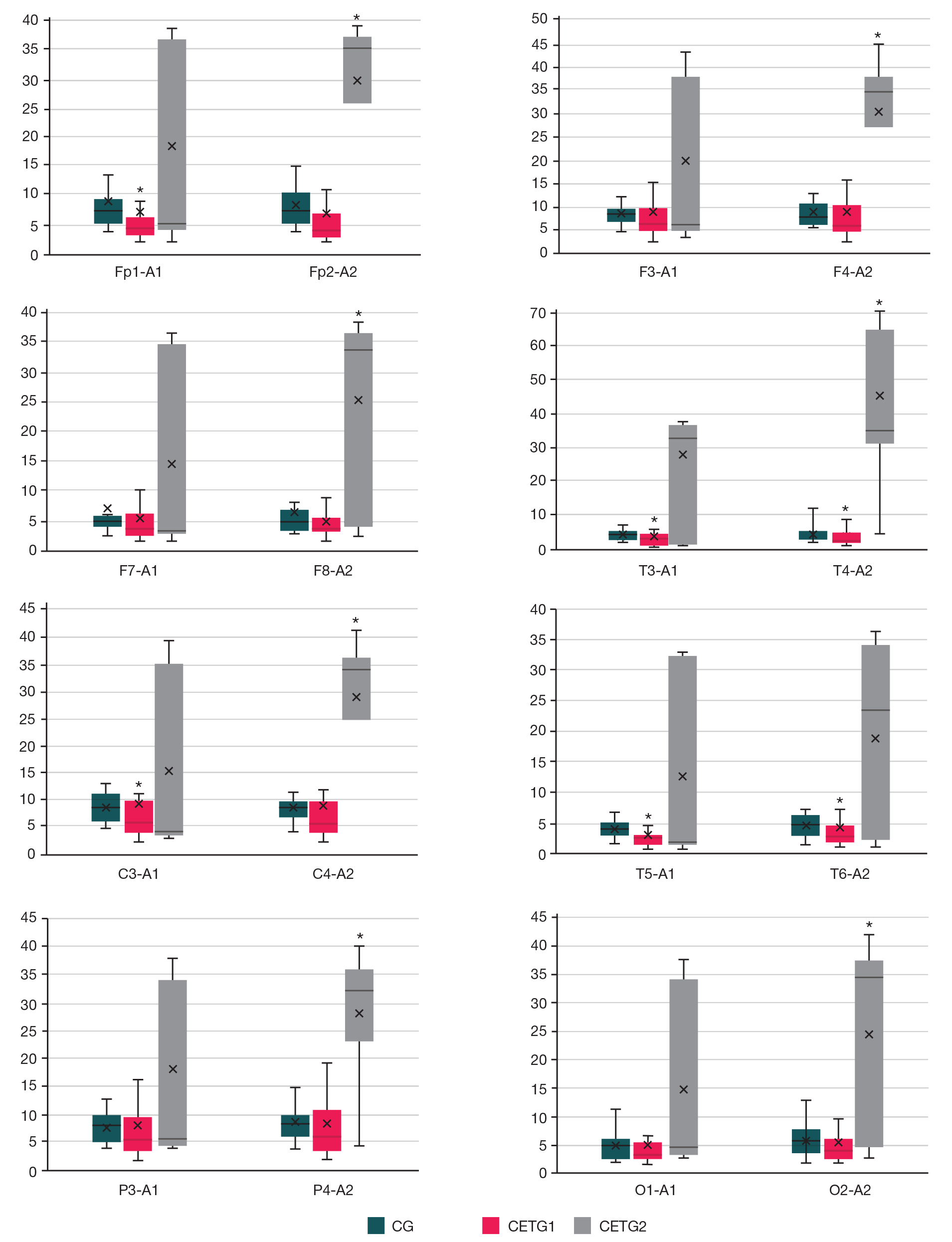
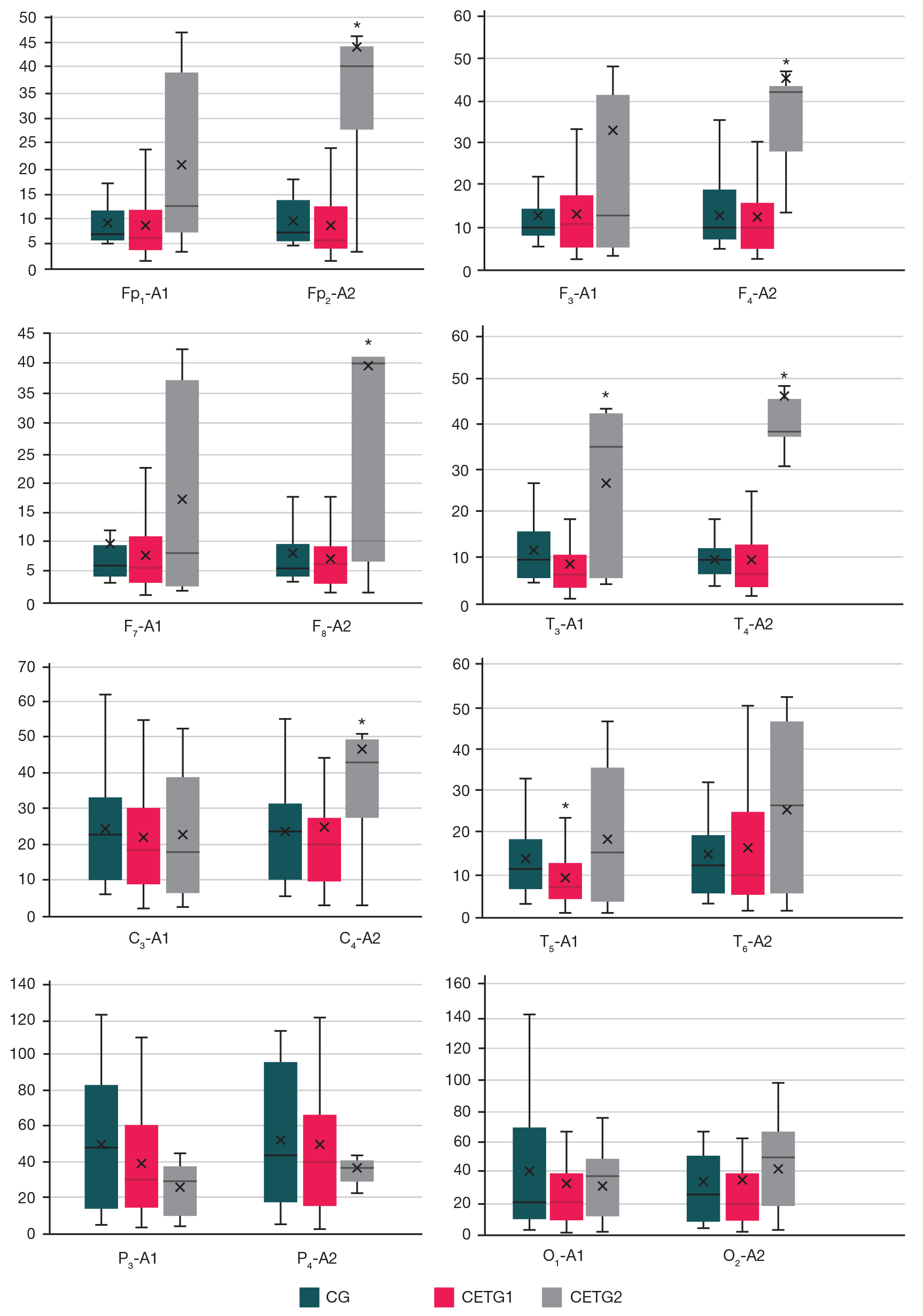
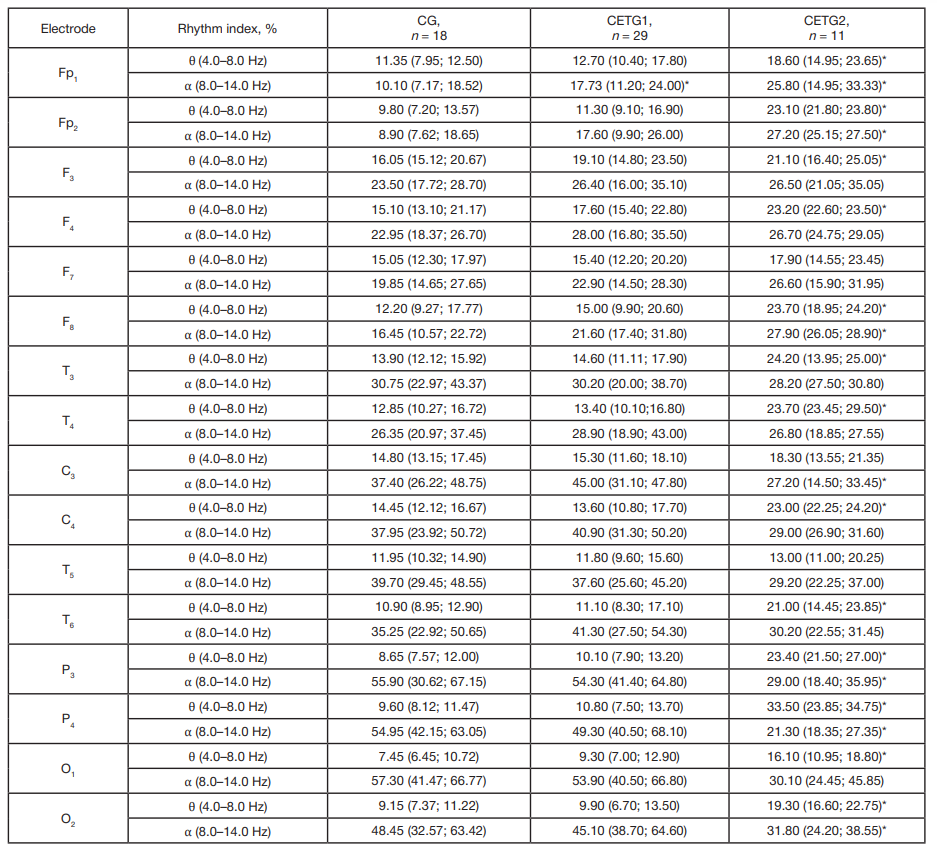
Impact of persistent cold stress on spectral characteristics of EEG alpha and theta rhythms in military academy cadets
1 University of Tyumen, Tyumen, Russia
2 Proshlyakov Tyumen Higher Military Engineer Command School, Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation, Tyumen, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Sergey N. Tolstoguzov
Volodarskogo, 6, Tyumen, 625003, Russia; ur.nmtu@vozugotslot.n.s
Author contribution: Tolstoguzov SN — research procedure, data analysis, manuscript writing; Fisher TA — data analysis, manuscript writing; Naida YuV — research procedure; Lepunova ON — data analysis.
Compliance with the ethical standards: the study was approved by the Ethics Commitee of the University of Tyumen (protocol № 11 dated 19 February 2024). All patients submitted the informed consent to stady participation.