This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
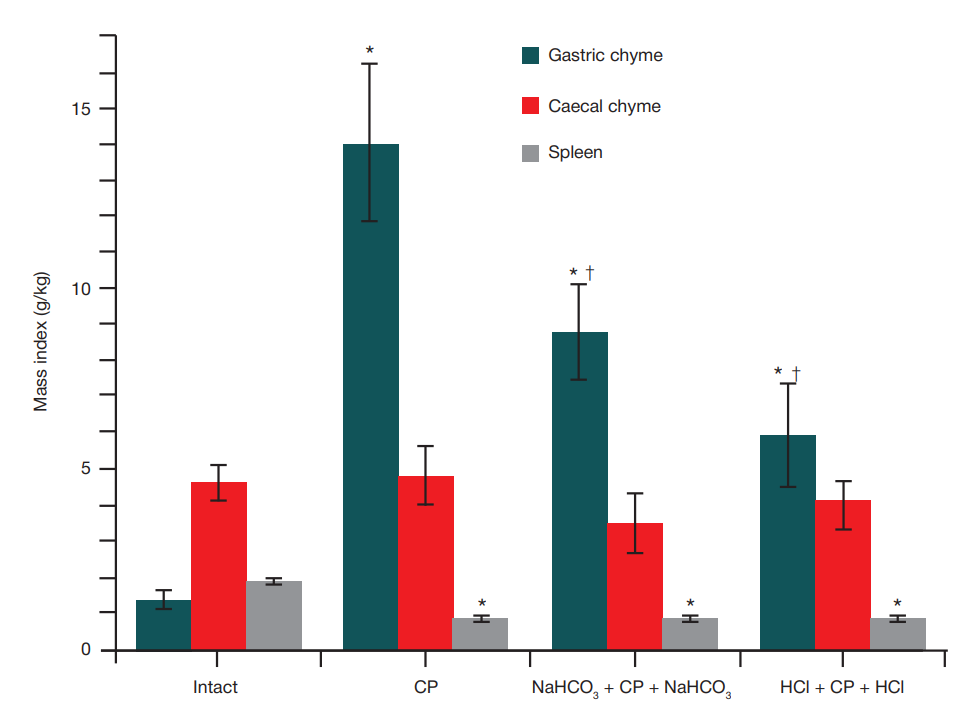
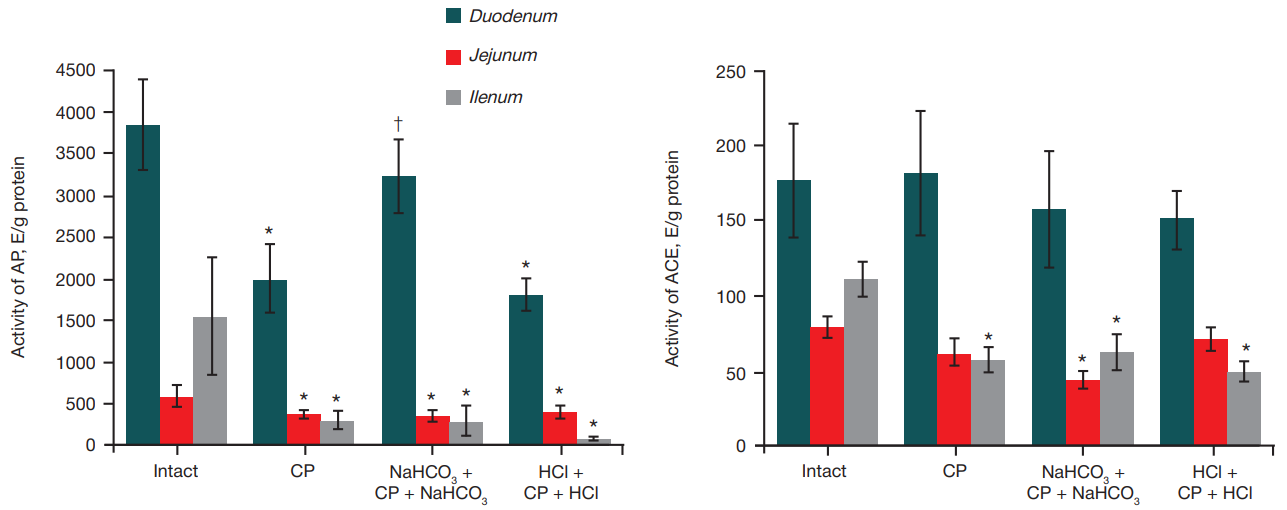
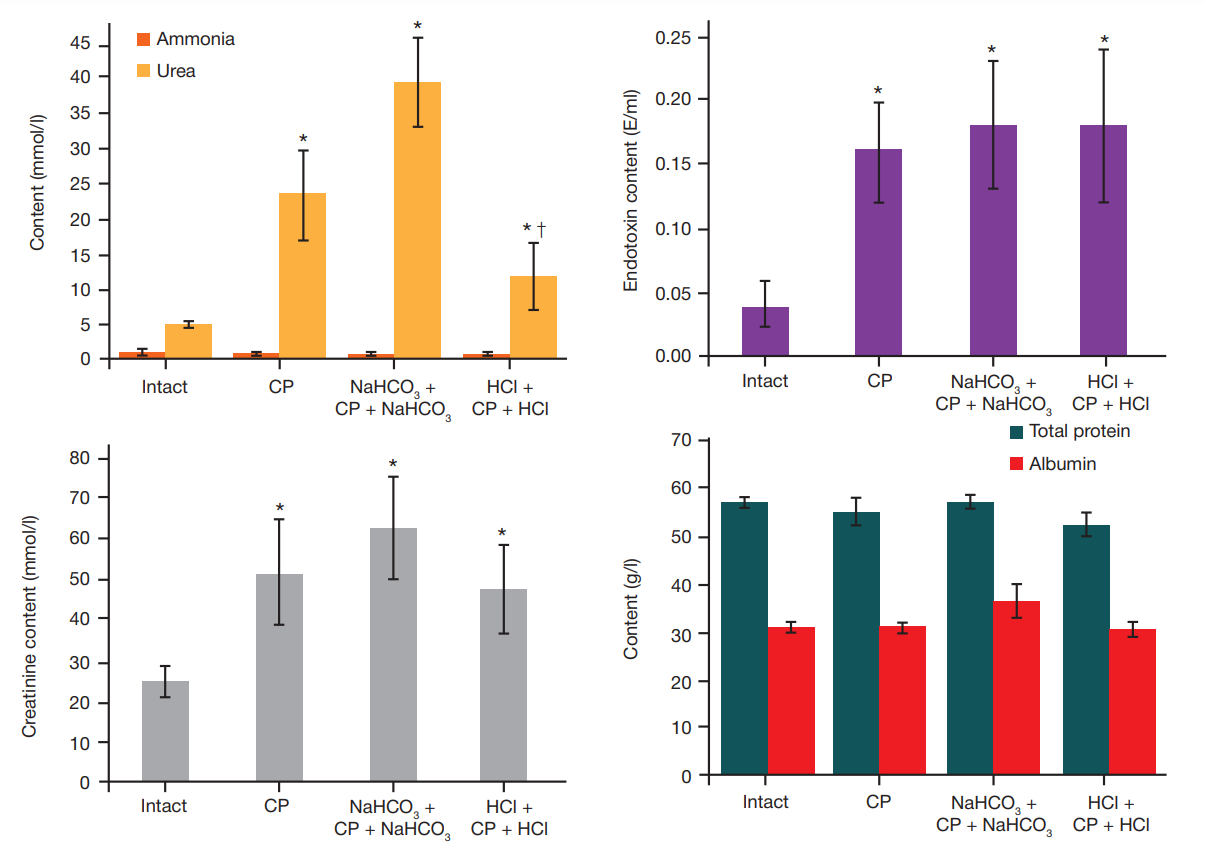
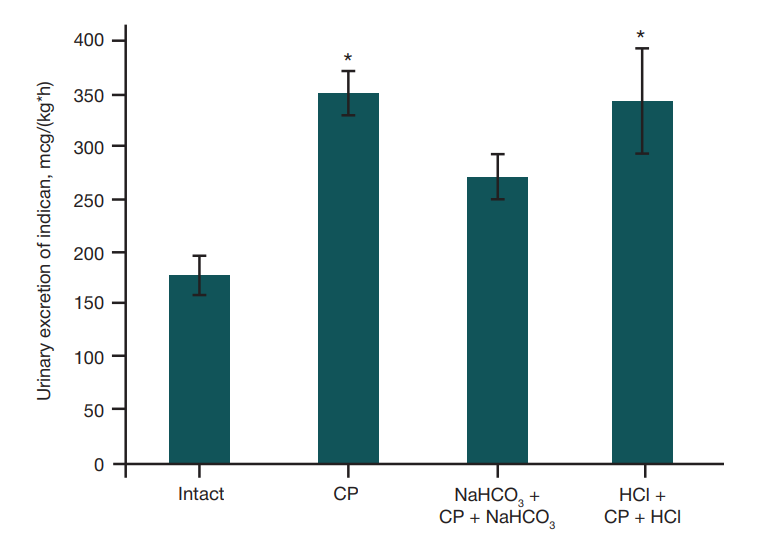
Effect of sodium bicarbonate or hydrochloric acid intragastric administration on gut-derived endotoxemia in rats receiving cyclophosphamide myeloablative conditioning
1 Golikov Research Clinical Center of Toxicology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
2 State Scientific Research Test Institute of the Military Medicine of Defense Ministry of the Russian Federation, Saint-Petersburg, Russia
Correspondence should be addressed: Tatiana B. Pechurina
Lesoparkovaya, 4, Saint-Petersburg, 195043, Russia; ur.tsil@97tat
Author contribution: Vakunenkova OA — experimental part of the study; Zolotoverkhaya EA — blood biochemistry testing; Pechurina TB — tissue biochemistry testing; Schäfer TV — experimental part of the study, data processing and visualization, developing the experimental model; Ivnitsky JuJu — research design, developing the experimental model, data interpretation and discussion. All authors contributed to discussion, manuscript writing and editing.
Compliance with ethical standards: the study was compliant with the principles of bioethics adopted by the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes.